
- #Absolute value on graphmatica how to
- #Absolute value on graphmatica plus
- #Absolute value on graphmatica free
2, − 1Įrror, invalid input: `simpl/abs` expects its 2nd argument, a2, to be of type algebraic, but received Array(1. The derivative of the absolute value of an rtable cannot be determined, so an error results.Ībs 1, rtable 1. Both the answers x -5/2 and x 1/4 are correct and acceptable. Substituting x -5/2 and x 1/4 into the original equation results in true statements. Substitute x -5/2 and x 1/4 in the given absolute value equation.
#Absolute value on graphmatica how to
To find the absolute value of a Matrix, use the absolute value function as written in 1-D Math, to avoid confusion between the function abs and the determinant of the Matrix.Ībs Array 1. The picture shown below explains how to solve the equations in which we have absolute value sign on both sides. The absolute value of a complex number is the modulus.Īssume u, positive : simplify expr When n is known, the expression is automatically simplified to the appropriate expression in a derivative of either signum or abs. Higher order derivatives of abs are denoted by abs(n, x), where n is a positive integer.
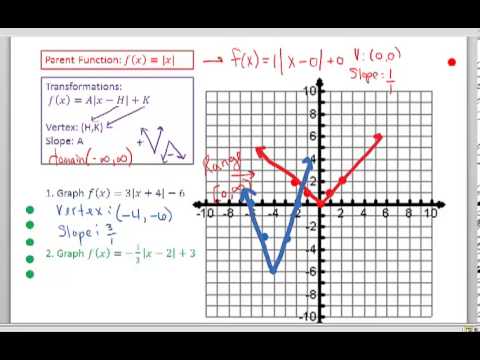
You could view this as the same thing as y is equal to the absolute value of x minus negative three.
#Absolute value on graphmatica plus
If you replace your x, with an x plus three, this is going to shift your graph to the left by three. Now in previous videos we have talked about it.
#Absolute value on graphmatica free
This Absolute Value Calculator Basics: Complete Guide includes several examples, a step-by-step tutorial, an animated video mini-lesson, and a free worksheet and answer key. Neither first order nor higher order derivatives of abs can be determined if x is an rtable. Y is equal is to the absolute value of x plus three. Absolute Value Calculator Skill 3: How to graph absolute value equations and expressions on your graphing calculator (TI-83, TI-84, or TI-84 plus). Then the same is true for f ( x), and so, any unit vector u will work. Here is a set of practice problems to accompany the Absolute Value Equations section of the Solving Equations and Inequalities chapter of the notes for Paul Dawkins Algebra course at Lamar University. Being an integral of a continuous function, this implies that f ( x) is identically zero. This is signum(x) for all non-0 real numbers, and is undefined otherwise. If a b f ( x) d x 0, then (1) implies a b f ( x) d x 0. Programs included Graphmatica: an excellent graphing utility Equation grapher and. The absolute value in maths is defined as the value which describes the distance of a number on the number line from 0 without taking into consideration which direction from zero the number lies.
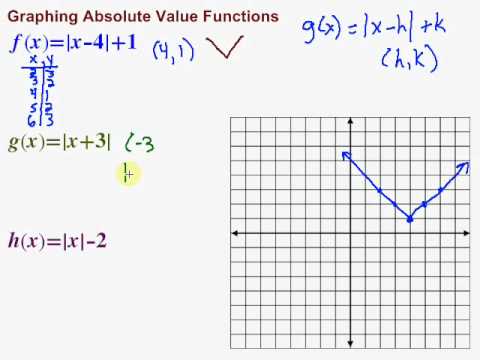
The derivative of abs is denoted by abs(1, x). The user can thus easily extend the functionality of abs. If x includes a function f, then abs will attempt to execute the procedure abs/f to determine the absolute value of the corresponding part of x. If x is an rtable (Array, Matrix, or Vector), the abs function applies the abs function to each entry in the table, and returns the resulting rtable. For example, abs(-11) is equivalent to −11. You can enter the command abs using either the 1-D or 2-D calling sequence. The abs function returns the absolute value of the expression x. The graph of absolute value function has a shape of V or inverted V.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
